2200 AW Grimes Blvd, Suite 100 Round Rock, TX 78665
Can a Deep Cavity Heal on Its Own?
Cavities are a common dental issue that can lead to more severe oral health problems if not addressed properly. When discussing cavities, many people wonder whether a deep cavity can heal on its own. Understanding the nature of tooth decay and the limitations of self-healing is crucial for maintaining good oral health. In this blog, we will explore the characteristics of deep cavities, the factors influencing their progression, and what actions you can take to protect your teeth.
What is a Cavity?
A cavity, also known as dental caries, is a decayed area of a tooth that results from the demineralization of the enamel and dentin due to acids produced by bacteria in dental plaque. Cavities can vary in severity:
- Early-stage cavities: Often affect only the enamel and can potentially be reversed with good oral hygiene and fluoride treatment.
- Moderate cavities: Extend into the dentin layer and can cause discomfort or sensitivity.
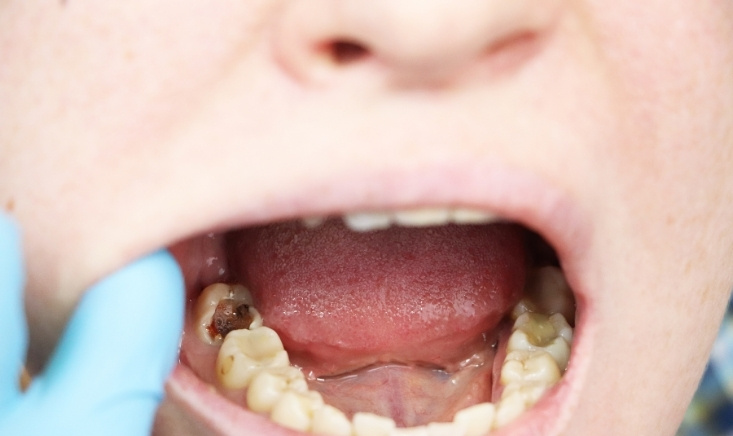
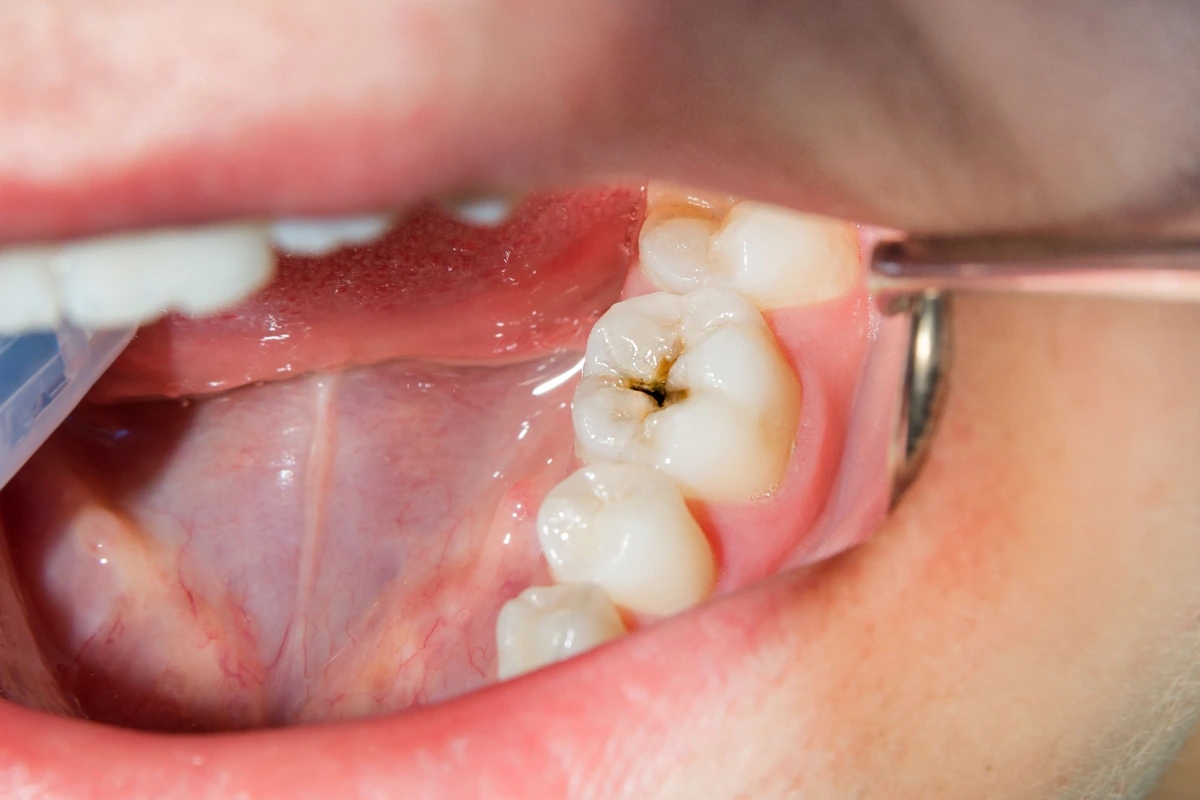
- Deep cavities: Involve significant decay that may reach the pulp of the tooth, leading to severe pain and potential infection.
Can a Deep Cavity Heal on Its Own?
The short answer is no; a deep cavity cannot heal on its own. Once a cavity progresses to the point of involving the dentin or pulp, it cannot simply reverse itself without professional dental intervention. Here’s why:
- Structural Damage: A deep cavity creates a physical hole in the tooth structure, which cannot regenerate on its own. Unlike some body tissues, enamel and dentin do not have regenerative properties.
- Bacterial Infection: Deep cavities often harbor bacteria that can cause infection. The longer the cavity remains untreated, the greater the risk of complications, such as abscesses or the spread of infection to surrounding tissues.
- Pulp Involvement: When decay reaches the pulp, it can lead to pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp), resulting in severe pain and requiring treatment like a root canal or extraction.
Factors Influencing Cavity Progression
Several factors can influence whether a cavity progresses to a deeper level, including:
- Oral Hygiene Practices: Maintaining a good oral hygiene routine is essential in preventing the progression of cavities. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help remove plaque and food particles, reducing the risk of decay.
- Diet: A diet high in sugar and acids can contribute to the formation and progression of cavities. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars, producing acids that erode tooth enamel. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks can help prevent further damage.
- Saliva Production: Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids and providing essential minerals to teeth. Reduced saliva flow, due to medications or medical conditions, can increase the risk of cavities. Staying hydrated and chewing sugar-free gum can stimulate saliva production.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Regular dental visits allow for early detection of cavities. Dentists can identify problems before they become severe and provide necessary treatments to halt progression. Most people should see their dentist every six months.
Signs of a Deep Cavity
Recognizing the signs of a deep cavity is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent Toothache: Ongoing pain in the affected tooth, especially when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to temperature changes or certain foods.
- Visible Holes or Dark Spots: Noticeable holes in the tooth or darkening of the enamel.
- Swelling or Abscess: Swelling in the gums or the formation of a pus-filled bump near the tooth.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek dental care promptly to prevent complications.
What to Do if You Have a Deep Cavity
If you suspect you have a deep cavity, here are the steps you should take:
1. Schedule a Dental Appointment: Consult a dentist as soon as possible. They can assess the extent of the decay using X-rays and determine the appropriate treatment.
2. Follow Recommended Treatments: Depending on the severity of the cavity, your dentist may recommend:
- Fillings: For moderate cavities, fillings can restore the tooth’s structure and function.
- Root Canals: If the pulp is affected, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and preserve the tooth.
- Crowns: In cases of significant damage, a crown may be placed to protect and restore the tooth.
3. Practice Good Oral Hygiene: After treatment, maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine to prevent future cavities. Brush, floss, and consider using fluoride products as advised by your dentist.
4. Make Dietary Adjustments: Reducing sugar intake and incorporating tooth-friendly foods can promote better dental health. Foods high in calcium, phosphorus, and fiber can help strengthen teeth.
A deep cavity cannot heal on its own. If you suspect that you have a deep cavity, it is essential to seek professional dental care to address the issue effectively. By maintaining good oral hygiene, making dietary changes, and attending regular dental check-ups, you can help prevent cavities and maintain your oral health. Remember, early intervention is key to preserving your teeth and preventing more serious complications. Don’t wait for a deep cavity to worsen—take action today to protect your smile!