2200 AW Grimes Blvd, Suite 100 Round Rock, TX 78665
Dental Care for Diabetics: Preparing for Root Canal Treatment
Living with diabetes often means paying extra attention to various aspects of your health, and dental care is no exception. Suppose you’re a diabetic preparing for a root canal treatment. In that case, it’s crucial to understand how diabetes can impact your oral health and what steps you can take to ensure a successful and comfortable procedure. In this guide, we’ll delve into the essential aspects of dental care for diabetics undergoing root canal treatment, providing you with valuable insights and tips to navigate this specific aspect of your health journey.
The Interconnection: Diabetes and Oral Health
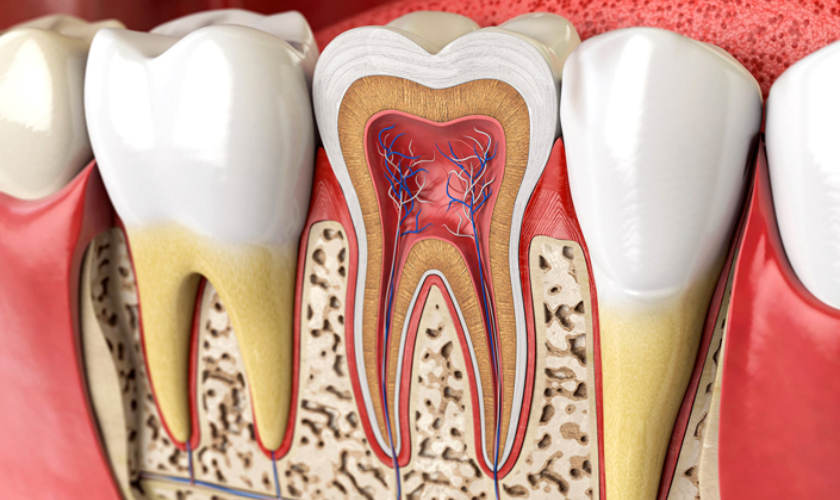
Before delving into the specifics of root canal treatment, let’s briefly explore the intricate relationship between diabetes and oral health. Diabetes can affect the gums and teeth, making individuals more susceptible to oral health issues such as gum disease, tooth decay, and infections. Proper oral hygiene becomes paramount, especially when facing dental procedures like root canal treatment.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
One of the primary concerns for diabetics undergoing any dental treatment is managing blood sugar levels. Fluctuations in blood glucose levels can impact the body’s ability to heal, potentially affecting the success of the root canal procedure. Prior to the treatment, work closely with your healthcare team to ensure your blood sugar levels are well-controlled.
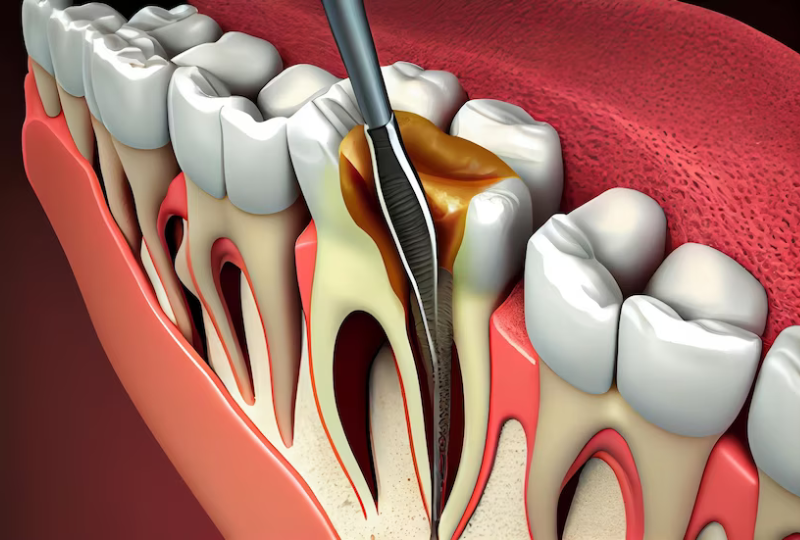
Preparing for Root Canal Treatment
1. Consultation with Your Dentist
Before embarking on the root canal journey, schedule a comprehensive consultation with your dentist. Discuss your diabetes management plan and any specific concerns related to the procedure. Your dentist will assess your oral health, ensuring that any pre-existing issues are addressed before initiating the root canal treatment.
2. Antibiotic Prophylaxis
Diabetics may be more susceptible to infections, making antibiotic prophylaxis a consideration before the root canal procedure. Your dentist will evaluate the necessity of antibiotics based on your overall health, ensuring that the risk of infection is minimized during and after the treatment.
3. X-Rays and Diagnostics
Accurate diagnostics are crucial for a successful root canal treatment. X-rays and other imaging tests help your dentist assess the extent of the dental issue and plan the procedure accordingly. Be sure to inform your dental team about your diabetic condition to tailor the diagnostic approach to your specific health needs.
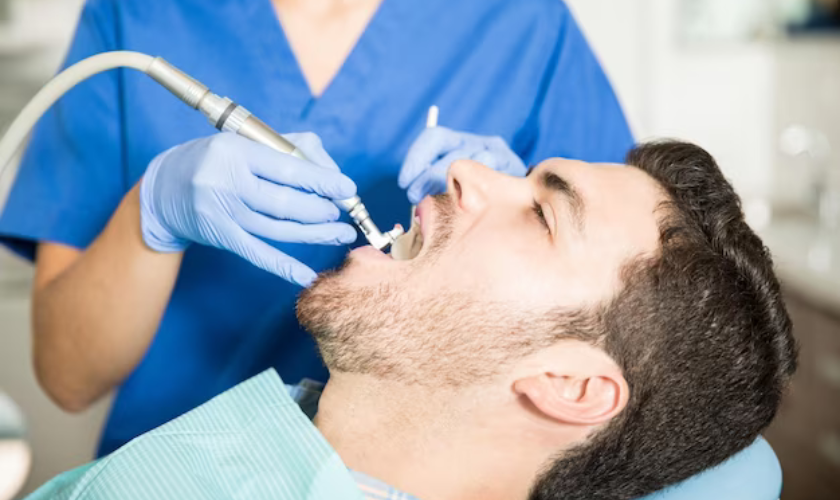
Navigating the Root Canal Procedure
1. Medication Management
During the root canal procedure, it’s essential to coordinate with both your dentist and healthcare team to manage your medications effectively. Certain medications may need adjustment or temporary discontinuation to ensure a smooth and safe dental experience.
2. Informed Consent
Understanding the procedure and potential risks is crucial for all patients, but it’s especially important for diabetics. Ensure you have a clear understanding of the root canal treatment, including any potential complications and post-treatment care instructions. This informed consent process is vital for your peace of mind and the success of the procedure.
3. Post-Treatment Care
Recovery after a root canal treatment is as important as the procedure itself. Diabetics should pay extra attention to post-treatment care, including oral hygiene practices and any prescribed medications. Regular follow-up appointments with your dentist will monitor the healing process and address any concerns promptly.
Maintaining optimal oral health is a collaborative effort, especially for individuals managing diabetes. By taking proactive steps, such as consulting with your dentist, managing blood sugar levels, and adhering to post-treatment care, you can navigate root canal treatment with confidence. Remember, your oral health journey is a vital component of your overall well-being. Consult with our experienced team to embark on a path that prioritizes both your dental and systemic health.